VIDEO CONFERENCE
George Politis ist422736, Kleanthis Tsesmetzidis ist422733
Instituto Superior Técnico
Av. Rovisco Pais, 1049-001 Lisboa, Portugal
E-mail: {gpolitis, kletsesm}@it.teithe.gr
Abstract
The first video conference attempt ever made was by NASA.Since then video conference has been more reachable to people.Thus it has affected society a lot. It is a big thing also in the market. Also it is a think that is continuously advancing and we expect to see a lot of changes in the future.
1.Introduction
We are going to discuss the things about video conference (VC). Video conference can be separate in three main categoriesRoom-based video conferencing, desktop video conferencing, telepresence or a combination. All these categories are in fact the same thing, communication with visual information. We are going to see how this thing evolved. Also we are going to discuss the technology that it is being used in video conference.
Another thing that we are going to analyse is the part of the Business. Such as business models.
More over, video conference has a direct impact on society so it would be discussed as well. For example how telemedicine has evolved and things like e-learning. Also how not only businesses but academic institutions are communicating through video conference. In advance the competition with products in the market will be mentioned. Finally which are the current trends on the market and what we are going to examine the new trends and predictions about the future. All though the terms of video telephony , video conference ,telepresence and video calls are not exactly the same, in they will be treated as same for the shake of simplicity.
Index Items -- video conference, Video telephony
2.History
The history of video conference begins from NASA. NASA was first used a point to point communication with two radio frequency UHF or VHF links, in both directions. This kind of communication is even being used today for communicate from distant locations for live reporting.The first commercial product was made by AT\&T and it was carrying the name "Picturephone". Even for that time(1970) it was really expensive since a single point-to-point connection costed 160\$/month. But gradually as the time passed the corporations saw the real potential for success and how can they increase their revenue with trans-Atlantic-like scale communication in video telephony. New protocols started to developed like NVP(1976) and PVP(1981). In 1982 there have already been installed video conferencing links in the U.S. by IBM for weekly inside-business meetings.
In the 80s video conference didn't take the country by storm due to the high cost of the service. In 1986 VC (Video Conference) service was offered by PictureTel for \$80.000 price available for 4 years with additional cost \$100 per hour line.
In the 90s
the tecnology had advanced and the market was ready for the VC after a lot of failed attempts for commercial VC products like Mitsubishis's still-picture phone.
The Internet Protocol(IP) and new compression technics would permit desktop PC-based VC. After a few years services like NetMeeting, MSN Messenger and Yahoo Messenger were adopted by the audiences, since they were also free, although the quality wa very poor.
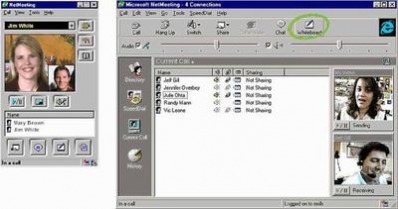
A point of reference in VC is the Apple Macintosh product "CU-SeeMe" in 1992. What made CU-SeeMe special was its outstanding performance for that time but more over Apple had made a VC product that was able to make multipoint connections. It was so successful product that in 1995 a version for Microsoft was build. By 1992 a lot of other companies took action like INRIA which set the foundation for the VC market. After this the first standard was about to be created by the International Telecommunication Union(ITU).
Speaking about standards, one of the first was the H.236 that set a smaller bandwidth transmission for low bit-rate communications.That time(1998) also the MPEG-4 standard was developed, which might not being used in the VC directly but its connection why previous standards like H.323 help to the interoperability with Video content and its transmission.
Not only in the market but also in universities and Research Centers like Cern VC became very popular. But also VC technology was used by reporters in the war of Afghanistan in 2001. In 2002 the Joint Video Team made the ITU-T H.264 protocol which standardized the compression in video for MPEG-4 but also for UTI-T.
The year that followed VC became very popular due to some simple reasons. Everyone could afford buy a PC with a web-cam, Broadband internet was accessible to more and more people. Finally free services like MSN messenger were accessible to most of the people. VC found its way into schools as the price of using this technology decreased.In these days the new trend is using Cloud-Base Delivery instead of Proprietary Hardware.\cite{nefsis}

The VC could be separated in two main kinds: Dedicated systems and Desktop .
The first one it is usually much bigger that the second. Telepresence is a kind
of a dedicated system. Whole rooms are dedicated for this purpose. Usually this kind of equipment is being bought by a company as a whole set of tools (i.e you cannot by your own camera from the local store). Fixed cameras are used the most of the times and video projectors or large screens are usually in a fixed position.
Also the room has some set of chairs which is also usually fixed. The reason that
dedicated system are like this is because they serve a specific purpose. For example they are used for bussinnes meetings which require to have an formal behaviour. Also usually in a telepresence system your are not only buying the hardware but you are also paying for having good video and voice quality without interuptions. That might seem not so important but many surveys suggested that after two or three fail calls (i.e skype calls) the people get frustrated and they
don't use the service.

On the other hand Desktop systems serve the perpose of every day user. They are much cheaper in terms of hardware and most of the times you don't have to pay even for the service(hangouts,skype,oovoo). The obvious drawbacks in Desktop systems are that the video quality is not so good and sometimes you cannot make a video call even if you try ten times or more.
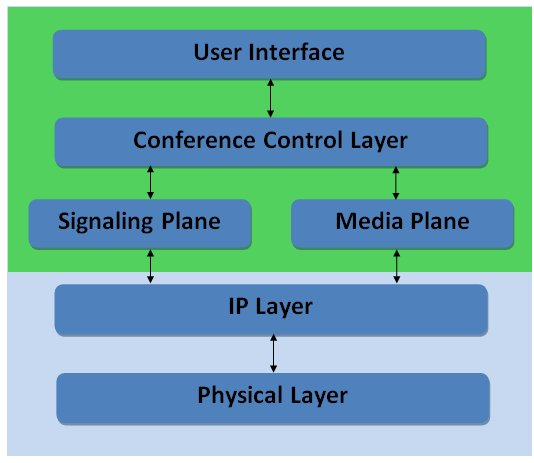
Conferencing layers
The components within a Conferencing System can be divided up into several different layers: User Interface, Conference Control, Control or Signal Plane, and Media Plane.
Videoconferencing User Interfaces (VUI) can be either graphical or voice responsive. Many in the industry have encountered both types of interfaces, and normally graphical interfaces are encountered on a computer. User interfaces for conferencing have a number of different uses; they can be used for scheduling, setup, and making a videocall. Through the user interface the administrator is able to control the other three layers of the system.
Conference Control performs resource allocation, management and routing. This layer along with the User Interface creates meetings (scheduled or unscheduled) or adds and removes participants from a conference.
Control (Signaling) Plane contains the stacks that signal different endpoints to create a call and/or a conference. Signals can be, but aren’t limited to, H.323 and Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) Protocols. These signals control incoming and outgoing connections as well as session parameters.
The Media Plane controls the audio and video mixing and streaming. This layer manages Real-Time Transport Protocols, User Datagram Packets (UDP) and Real-Time Transport Control Protocol (RTCP). The RTP and UDP normally carry information such the payload type which is the type of codec, frame rate, video size and many others. RTCP on the other hand acts as a quality control Protocol for detecting errors during streaming.
Multipoint videoconferencing Main article: Multipoint Control Unit Simultaneous videoconferencing among three or more remote points is possible by means of a Multipoint Control Unit (MCU). This is a bridge that interconnects calls from several sources (in a similar way to the audio conference call). All parties call the MCU, or the MCU can also call the parties which are going to participate, in sequence. There are MCU bridges for IP and ISDN-based videoconferencing. There are MCUs which are pure software, and others which are a combination of hardware and software. An MCU is characterised according to the number of simultaneous calls it can handle, its ability to conduct transposing of data rates and protocols, and features such as Continuous Presence, in which multiple parties can be seen on-screen at once. MCUs can be stand-alone hardware devices, or they can be embedded into dedicated videoconferencing units.
The MCU consists of two logical components: A single multipoint controller (MC), and Multipoint Processors (MP), sometimes referred to as the mixer. The MC controls the conferencing while it is active on the signaling plane, which is simply where the system manages conferencing creation, endpoint signaling and in-conferencing controls. This component negotiates parameters with every endpoint in the network and controls conferencing resources. While the MC controls resources and signaling negotiations, the MP operates on the media plane and receives media from each endpoint. The MP generates output streams from each endpoint and redirects the information to other endpoints in the conference. Some systems are capable of multipoint conferencing with no MCU, stand-alone, embedded or otherwise. These use a standards-based H.323 technique known as "decentralized multipoint", where each station in a multipoint call exchanges video and audio directly with the other stations with no central "manager" or other bottleneck. The advantages of this technique are that the video and audio will generally be of higher quality because they don't have to be relayed through a central point. Also, users can make ad-hoc multipoint calls without any concern for the availability or control of an MCU. This added convenience and quality comes at the expense of some increased network bandwidth, because every station must transmit to every other station directly.
Standards The International Telecommunications Union (ITU) (formerly: Consultative Committee on International Telegraphy and Telephony (CCITT)) has three umbrellas of standards for videoconferencing: ITU H.320 is known as the standard for public switched telephone networks (PSTN) or videoconferencing over integrated services digital networks. While still prevalent in Europe, ISDN was never widely adopted in the United States and Canada.[citation needed] ITU H.264 Scalable Video Coding (SVC) is a compression standard that enables videoconferencing systems to achieve highly error resilient Internet Protocol (IP) video transmissions over the public Internet without quality-of-service enhanced lines.[28] This standard has enabled wide scale deployment of high definition desktop videoconferencing and made possible new architectures, which reduces latency between the transmitting sources and receivers, resulting in more fluid communication without pauses. In addition, an attractive factor for IP videoconferencing is that it is easier to set up for use along with web conferencing and data collaboration. These combined technologies enable users to have a richer multimedia environment for live meetings, collaboration and presentations. ITU V.80: videoconferencing is generally compatibilized with H.324 standard point-to-point videotelephony over regular plain old telephone service (POTS) phone lines. The Unified Communications Interoperability Forum (UCIF), a non-profit alliance between communications vendors, launched in May 2010. The organization's vision is to maximize the interoperability of UC based on existing standards. Founding members of UCIF include HP, Microsoft, Polycom, Logitech/LifeSize Communications and Juniper Networks
4.Social
The last 20th year the human communications have undertaken a very big change. People are able to communicate much cheaper . First the e-mail came to change the world as people where able for first time to communicate with people from other place of the world. Second chat rooms and instant messaging took all over the place. Then video-telephony. People were able to see relatives and other people face to face. Skype was one of the free applications that revolutionized people's communication. Video Telephony(VT) took over the world due to the easy way to connect people. The changes that this technology has brought are many. The most significant application have to do with distant places. These days we are talking about telemedicine and tele-psychotherapy. Now a days people in distant areas are able to take measurements like diabetes and talk with their doctors many miles away. Also it is become more popular among people to have psychotherapy sessions through skype. Now people that live at villages can access to these services. Not only that but people that afraid of the social judgement can now more easily talk to a person. But also at simpler thing. Nowadays due to the incremented mobility a lot of people that went abroad for studies or work can now talk with their beloved ones just with their smart phone and a wifi connection. No phone needed or charges unlike old time VC. Another thing is the massive classes that they are talking place in places like china. Due to the unbalance rate of the population growth and the available English teachers nowadays there are classes for two thousand people. More over studies suggest that the e-learning study can be as efficient as the traditional learning if it is in a regular basis. One of the most well know uses of video-conference is in businesses and in academic institutions.
Now things like an election of a professor or a speech at a conference can be achieved easily and for free. Also in corporations like IT where people can work from distant places, VOIP telephony have facilitated a lot our lives. On the other hand, though it sound really appealing, sometimes it is not how it works. Although VC cuts down costs, the non visual communication results to non efficient communication.
i.e Someone is presenting his ideas and the colleagues are on social networks or checking their mails the same time. This kind of thing has been observed from many people that use a lot VC. So it is a trade of between saving time and have a valuable meeting between the colleagues. \cite{fastcompany}
One of the most well know uses of video-conference is in businesses and in academic institutions.
Now things like an election of a professor or a speech at a conference can be achieved easily and for free. Also in corporations like IT where people can work from distant places, VOIP telephony have facilitated a lot our lives. On the other hand, though it sound really appealing, sometimes it is not how it works. Although VC cuts down costs, the non visual communication results to non efficient communication.
i.e Someone is presenting his ideas and the colleagues are on social networks or checking their mails the same time. This kind of thing has been observed from many people that use a lot VC. So it is a trade of between saving time and have a valuable meeting between the colleagues. \cite{fastcompany}
It would be also useful to put it from the perspective of how the conversation in VC is carrying out. More specificity the characteristics of VC are limiting our ability of fluent communication in comparison with real communication. Factors like the frames per second, the position of the body make the conversation more difficult. Also the angle of the body is the same, so the body language is very much restricted.Not even to mention micro-gestures as a small lip movement which in real life someone can tell if the person who is speaking with, is lying or not. Moreover due to the nature of internet (packets and not dedicated lines like telephony) makes it vulnerable to errors which mean that the voice a lot of times might be corrupted. That is to mean that the conservators are in a king of situation , wait to hear the other and then respond, which in real life doesn't happen because we have much more interruptions. All these things make the communication with VC much more unnatural.That is why people still prefer the telephone, because they rely only on their voices instead of trying to adapt to this simulation of real conversation.
5.Competition
- Adobe Connect “Universal Voice: Enabling audio integration regardless of platform”
- Avistar “Integrated applications for unified collaboration”
- Cisco Unified Meeting Place “Enhance Productivity with Virtual Meetings” Conference Group “Global. Experienced. Customized.”
- DimDim “Web Conferencing That Just Works”
- Ekko Elluminate “Where Bright Ideas Meet”
- FlashMeeting
- GatherPlace “Effective Remote Communications”
- Gizmo5 Glance “Desktop Sharing With One Click”
- Google Video Chat
- GoToMeeting “Online Meetings Made Easy” World”
- HP SkyRoom “The visual sharing power to work from wherever you have network access”
- IBM SameTime “Your onramp to unified communications and collaboration”
- IChat
- ilinc “Web \& Video Conferencing” Conferencing Solution”
- iVisit “Meet Anywhere, Anytime for FREE”
- Logitech – Lifesize
- Logitech – SightSpeed
- MeBeam
- MegaMeeting “Video & Web Conferencing For ALL Of Us”
- Microsoft Office Live Meeting
- Microsoft Communicator
- Nefsis
- Netviewer Meet
- ooVoo “Amazingly simple crystal clear video chat”
- Palbee “World has never been smaller!”
- Paltalk
- Persony “Cost-effective Private Label Web/Video Conferencing”
- Polycom PVX
- Radvision SCOPIA “Delivering the Visual Experience”
- Saba Centra “The People Management Solution”
- Skype “Say, Hi World!” — You might also be interested to read our article here: VSee – Free Alternative to Skype Video Conference – Comparison
- SnapYap “Instant Video Calling and Video Messaging”
- Vawkr “Instant group video chat that you can paste anywhere”
- VeaMea “A Fresh Way To Communicate and Collaborate”
- Vidivic “Your partner in web conferencing”
- Vidsoft “Increase Productivity. Save Time and Money”
- Vidyo “Personal Telepresence” — You might also be interested to read our article here: VSee – Free Alternative to Vidyo Telepresence Business Video Conference – Comparison
- ViVu “Better than being there”
- VTEL Ipanel “All-In-One Room System”
- Vyew “Share Your View”
- Webex Wormhole Web Conference “Easy, Fast and Affordable Web Conferencing”
- Wimba “people teach people”
- WorldVuer “Touch the world”
- YuuGuu
- Zorap “Hang out and enjoy”
This is only a small list of all of the business solutions that they are available on the market a companied with a title slogan. That is to mean that there is a lot of competition out there both on the free and commercial services.
6.Future
 Google hangouts, the equivalent VoIP service is already available on chrome browser. Apple has do the same as it is available to make FaceTime calls via Safari. That is to mean that the companies are aiming rather on the browsers than a stand alone application. Also a great deal of attention is focus on mobile and tablet application. For some reason Microsoft released a major update for the skype application on iPad and iPhone.
But all these has to do with the current technology.
What have taken the technological world by storm is the oculus device for virtual reality. In fact is an advanced head set that can be used in multiple fields such as gaming but also in VoIP. The reason why it is the talk of the town
Is because people will be able to sit in virtual rooms and communicate like sitting next to each other. That brings communication to a very different level. It facilitates a lot the communication process. This technology is very prominent, the people of oculus are promising that the users will be able to interact with objects. People will be more flexible in their communication as they will be able to interact with physical objects like white boards. That will also will facilitate professions like architects that deal a lot with 3d structures. There is a big future in this area.
What also show that there is in general a lot of future in video conference in the numbers? Statistics show that a lot of money are being invested and the profits from VoIP telephony are rising.
Google hangouts, the equivalent VoIP service is already available on chrome browser. Apple has do the same as it is available to make FaceTime calls via Safari. That is to mean that the companies are aiming rather on the browsers than a stand alone application. Also a great deal of attention is focus on mobile and tablet application. For some reason Microsoft released a major update for the skype application on iPad and iPhone.
But all these has to do with the current technology.
What have taken the technological world by storm is the oculus device for virtual reality. In fact is an advanced head set that can be used in multiple fields such as gaming but also in VoIP. The reason why it is the talk of the town
Is because people will be able to sit in virtual rooms and communicate like sitting next to each other. That brings communication to a very different level. It facilitates a lot the communication process. This technology is very prominent, the people of oculus are promising that the users will be able to interact with objects. People will be more flexible in their communication as they will be able to interact with physical objects like white boards. That will also will facilitate professions like architects that deal a lot with 3d structures. There is a big future in this area.
What also show that there is in general a lot of future in video conference in the numbers? Statistics show that a lot of money are being invested and the profits from VoIP telephony are rising.
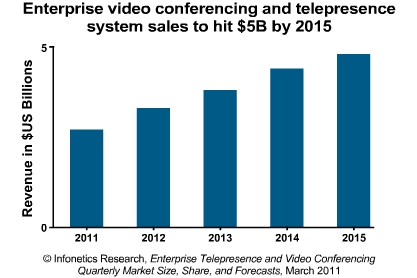 That has to do with the increase to the video quality and the cost that they are falling. One of the main factors why companies use more and more the video conference communication is due to the fact that in our age there are a lot of employees that work miles apart. So video conferencing cuts down the travel costs.
A web can see from the research conducted by the ”
Infonetics Research” enterprises are going to buy more and more
Video conference and telepresence products.
That has to do with the increase to the video quality and the cost that they are falling. One of the main factors why companies use more and more the video conference communication is due to the fact that in our age there are a lot of employees that work miles apart. So video conferencing cuts down the travel costs.
A web can see from the research conducted by the ”
Infonetics Research” enterprises are going to buy more and more
Video conference and telepresence products.
Getting into more technical stuff we are also waiting for the future a lot of changes in VC in mobiles. That is because of the great acceptance of the LTE networks. LTE mobile networks provide grater data capacity, as a matter of fact with this technology we are able to use HD voice which makes the video calls through mobiles much more better. In 2020 we are expecting the adoption of 5G networks which will bring much better performance in VC conference for smartphones.
References
- http://www.nefsis.com/best-video-conferencing-software/video-conferencing-history.html
- http://www.html5rocks.com/en/tutorials/webrtc/basics/
- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/WebRTC
- http://www.fastcompany.com/3006419/can-next-generation-video-conferencing-change-way-we-communicate
- Slovak, P. (2007). Effect of Videoconferencing Environments on Perception of Communication.} Cyberpsychology: Journal of Psychosocial Research on Cyberspace, 1(1), article 1.
- The impact of Video Conferencing on Distance Education: A University of Namibia Case Study Trudie Frindt , Continuing Education
- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Videoconferencing
- http://vsee.com/blog/484/
- http://www.tokbox.com/blog/firefox-hello-mozilla-enhances-opentok-powered-video-chat-service/
- http://venturebeat.com/2014/10/16/firefox-34-beta-arrives-with-firefox-hello-calling-by-telefonica-chromecast-tab-mirroring-from-android/
- http://www.cnet.com/news/firefox-hello-adds-video-chat-to-mozillas-browser/
- http://www.oculus.com/rift/
- http://www.webex.com/
- http://searchunifiedcommunications.techtarget.com/feature/Video-conferencing-adoption-Tracking-trends-and-deployment-strategies