Word about technology
Technology drives mobile multimedia with new means to communicate, cache, process, and display multimedia content:
Connectivity: New means to communicate enable new services.
Memory and persistent storage: Evolving memory technology allows caching of more content and offline processing, thus creating the illusion of instant access to interactive remote content.
Processing: More processing resources with less power consumption allow rendering of more complex multimedia content.
Display: Visualizing multimedia content demands for cheap high-resolution displays that comply with 'mobile' requirements (ruggedness, temperature, etc.).
Coming to details
A key element to enable mobile multimedia services is a wireless broadband communication channel. There are three major groups:
Terrestrial Networks
Satellite Broadcast Networks
Cellular Networks
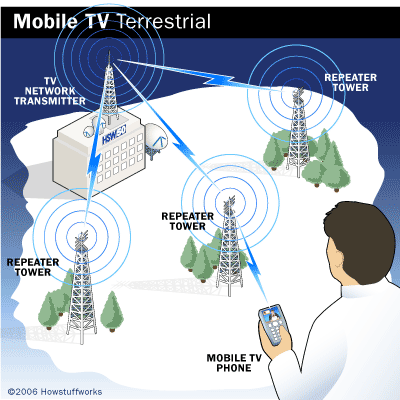
Terrestrial Networks
DVB-T (Digital Video Broadcasting - Terrestrial) is the terrestrial variant of the DVB standard for digital TV, radio, and data broadcast services. The key features are high bandwidth efficiency, undisturbed reception, better picture quality compared to analog TV, and the capability to broadcast data services. Read more about DVB-T...
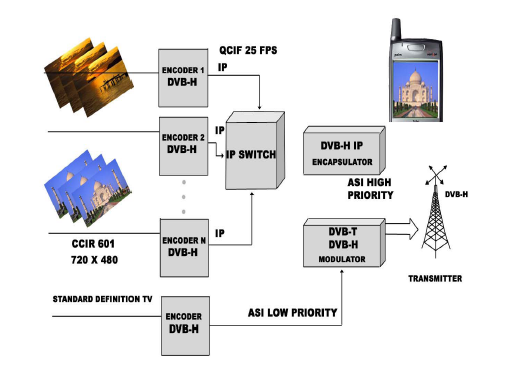
DVB-H (Digital Video Broadcasting - Handheld) is one of three prevalent mobile TV formats. It is a technical specification for bringing broadcast services to mobile handsets. It can offer a downstream channel at high data rates which can be used as standalone or as an enhancement of mobile telecommunication networks which many typical handheld terminals are able to access anyway. Read more about DVB-H...
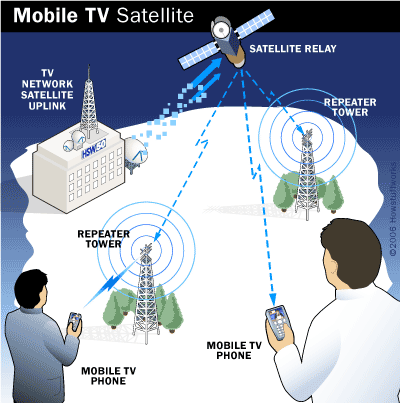
Satellite Broadcast Networks
DVB-SH (Digital Video Broadcasting - Satellite services to Handhelds) is a physical layer standard for delivering IP based media content and data to handheld terminals such as mobile phones or PDAs, based on a hybrid satellite/ terrestrial downlink and for example a GPRS uplink. The DVB-SH system was designed for frequencies below 3 GHz, supporting UHF band, L Band or S-band. DVB-SH architecture is shown in picture below. Read more about DVB-SH...
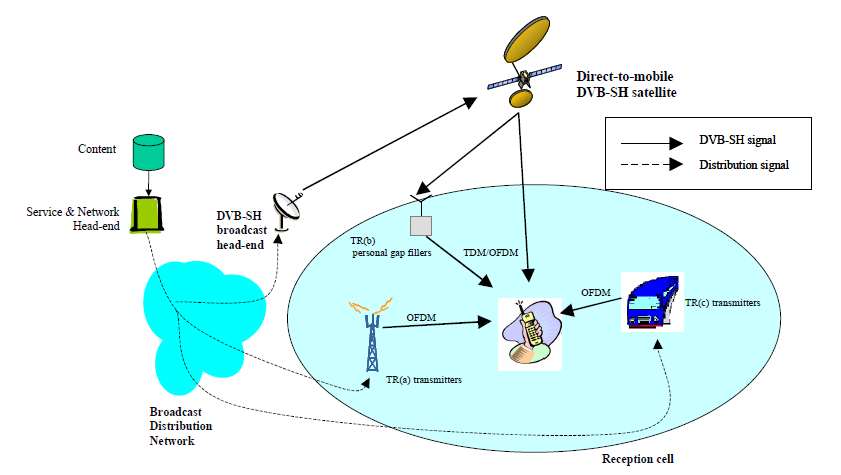
Cellular Networks
Today, 3G platforms systems offer a superior streaming capabilities for TV distribution, either as unicast service (e.g. HSPA) or broadcast service (e.g. MBMS).
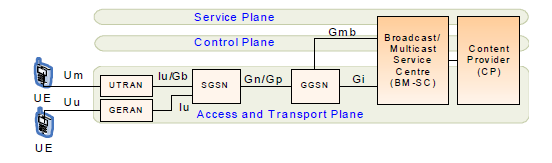
Multimedia Broadcast Multicast Service (MBMS)
In Release 6 3GPP standardized MBMS to support efficient
broadcast and multicast IP packet delivery in existing
UMTS and GPRS networks. MBMS allows two modes
of operation: the broadcast mode and the multicast mode. In picture belowe - MBMS architecture.
Read more about MBMS...